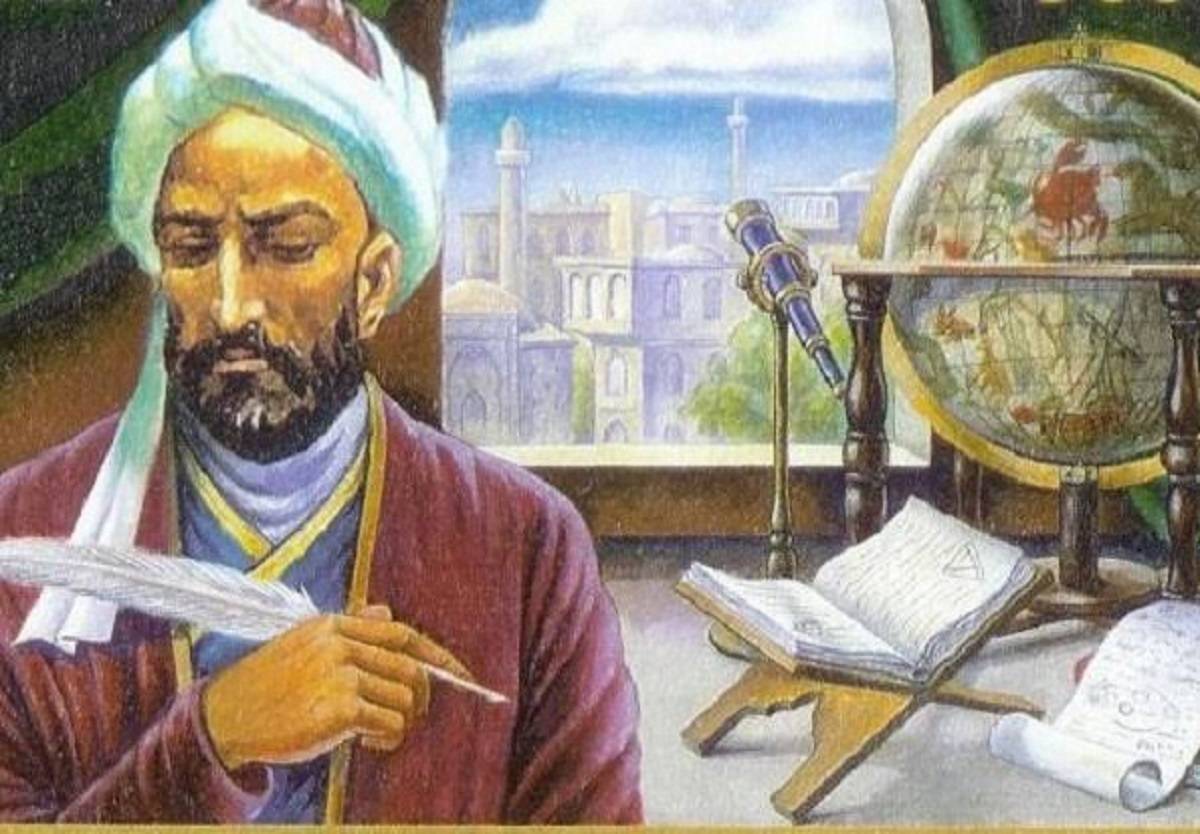
Muhammad ibn Muhammad ibn Hasan al-Tūsī was born on 18 February in 1201 in Tūs, Khorasan. Al Tusi is the prominent Muslim Scholar who is better known as Nasīr al-Dīn al-Tūsī. His name is distinct as a Muslim Persian scholar. He served as a prolific writer in diversified fields of science and philosophy. Moreover, he was also an astronomer, mathematician, physicist, philosopher, and theologian.

Background and Education
Al-Tūsī belongs to a family of learned scholars and his father and uncles influenced him to go towards the Islamic religious sciences along with the rational sciences. He preferred to study philosophy and mathematics in his hometown Tūs. However, he traveled to Nīshāpūr after the year of 1213 for continuing his education in the fields of sciences, medicine, and philosophy.
During his study, he preferred to learn the works of Ibn Sīnā and his work put a great influence on Al Tusi. Further, he traveled to Iraq to pursue his education in legal theory in Mosul in-between years of 1223 and 1232. His major contribution to astronomy is the invention of a geometrical technique recognized as the Tusi-couple. It served as a solution for the study of the latitudinal motion of the inferior planets.
His Books
As a famous Muslim scholar, Al-Tūsī wrote over 150 works. His books are in Arabic and Persian including the subjects of mathematical sciences, Muslim scholar philosophy, and the religious sciences. It includes fiqh, kalām, and Sufism. With his influential works in different fields, he acquired the titles of khwāja (recognized scholar and teacher), ustādh al-bashar (teacher of mankind), and al-mu’allim al-thālith (the third teacher, after Aristotle and Al-Fārābī). He also served as the administrator of the Islamic major astronomical observatory of Marāgha located in northern Iran.
His writings are both synthetic and original. His famous recensions is tahārīr. It highlights early Islamic scientific works including significant and original commentaries. This work includes Euclid’s Elements, Ptolemy’s Almagest, and mutawassitāt. Al Tusi’s other prominent works include books on logic, ethics, as well as a famous commentary on a philosophical work of Ibn Sīnā.
Quick Life Outlook
He passed away on 26 June 1274 in Baghdad at the age of 73. His influential work “Al-Tusi’s model for the planetary system” is prominent in the scientific world. It was greatly useful until the expansion of the heliocentric Copernican model.
However, Al-Tusi’s contribution to astronomy became the reason for the construction of astronomical instruments like the astrolabe. This instrument was effectively important in the Islamic world for calculating the Qibla. It also allows to find the correct time to offer prayer.
Al-Tusi is the first astronomer that mentioned the composition of Milky Way. He stated that Milkyway carries a large number of small and clustered stars. This was a scientific fact later proved by Galileo Galilei in 1610 using a telescope.
Al Tusi’s accomplishments and works are rememberable in the world of science. Al Tusi is a Muslim scholar who inspired masses with his inventions. Do you have more info on his life and work? Then share with us.